| | | | | | |
|
|
| |
| ... |
| This unit on weather, climate, and water cycling is broken into four separate lesson sets. In the first two lesson sets, students explain small-scale storms. In the third and fourth lesson sets, students explain mesoscale weather systems and climate-level patterns of precipitation. Each of these two parts of the unit is grounded in a different anchoring phenomenon.
The unit starts out with anchoring students in the exploration of a series of videos of hailstorms from different locations across the country at different times of the year. The videos show that pieces of ice of different sizes (some very large) are falling out of the sky, sometimes accompanied by rain and wind gusts, all on days when the temperature of the air outside remained above freezing for the entire day. These cases spark questions and ideas for investigations, such as investigating how ice can be falling from the sky on a warm day, how clouds form, why some clouds produce storms with large amounts of precipitation and others don’t, and how all that water gets into the air in the first place. |
| ... |
| The OpenSciEd Instructional Model uses a storyline approach– a logical sequence of lessons that are motivated by students’ questions that arise from students’ interactions with phenomena. To help teachers and students advance through a unit storyline, the instructional model takes advantage of five routines—activities that play specific roles in advancing the storyline with structures to help students achieve the objectives of those activities. The routines typically follow a pattern as students kick off a unit of study, investigate different questions they have, put the pieces together from those investigations, and then problematize the next set of questions to investigate. Click here to view the complete 6.3 Weather and Climate Storyline document. 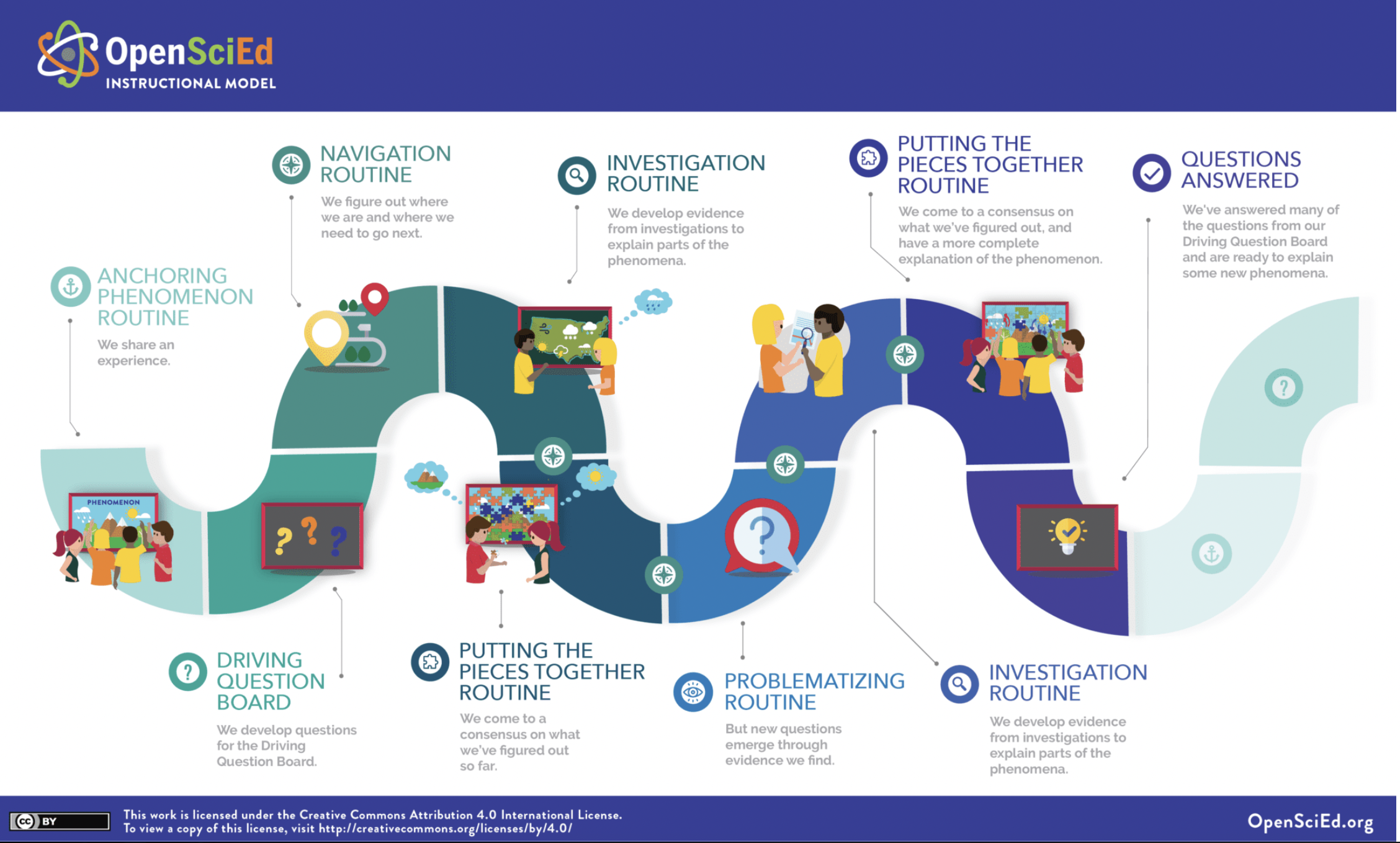
| In this first half of the unit, students investigate weather data specific to these events and the temperature profile of the atmosphere above the Earth’s surface. They conduct investigations into how sunlight affects the temperature of different surfaces and the air above them, and how this contributes to cloud formation and growth. They work with manipulatives, simulations, and labs to figure out how molecules in different phases change states under different conditions and they conduct investigations into why air moves the way it does as it is heated and cooled. The second half of the unit is anchored in the exploration of a weather report of a winter storm that affected large portions of the midwestern United States. The maps, transcripts, and video that students analyze show them that the storm was forecasted to produce large amounts of snow and ice accumulation in large portions of the northeastern part of the country within the next day. This case sparks questions and ideas for investigations around trying to figure out what could be causing such a large-scale storm and why it would end up affecting a different part of the country a day later. In the second half of the unit, students also investigate changes in weather conditions over the entire country over multiple days, as well as forecasts of three other storms that are forecasted to affect other parts of the country. They explore how the interactions of air masses, prevailing winds, proximity to the ocean, ocean currents, and surface elevation profiles work together to influence how much precipitation different regions receive. At the end of the second half of the unit, they apply their understandings to develop an explanation for why South America has a tropical rainforest in one part of the cont |
| ... |
| Structure and Properties of Matter Structure and Properties of Matter MS-PS1-4 Develop a model that predicts and describes changes in particle motion, temperature, and state of a pure substance when thermal energy is added or removed. MS-ESS2-4 Develop a model to describe the cycling of water through Earth’s systems driven by energy from the sun and the force of gravity. MS-ESS2-5 Collect data to provide evidence for how the motions and complex interactions of air masses results in changes in weather conditions. MS-ESS2-6 Develop and use a model to describe how unequal heating and rotation of the Earth cause patterns of atmospheric and oceanic circulation that determine regional climates. Copyright © 2001-2015 State of Michigan | Focal Disciplinary Core Ideas (DCIs): ESS2.C, ESS2.D, PS1.A, PS3.A
Focal Science and Engineering Practices (SEPs): Developing and Using Models; Planning and Carrying Out Investigations; Analyzing and Interpreting Data
Focal Crosscutting Concepts (CCCs): Patterns; Cause and Effect; Systems and System Models; Matter and Energy |
| ... |
| Please click here for a description of the big ideas that connect middle school NGSS (Achieve, 2017). | |
| ... |
| Please refer to OpenSciEd Unit and Lesson Level Documentation: A lesson-level performance expectation (LLPE) is a three-dimensional learning statement for each lesson aimed at highlighting the key student expectations for that lesson. Every OpenSciEd lesson includes one or more LLPEs. The structure of every LLPE is designed to be a three-dimensional learning, combining elements of science and engineering practices, disciplinary core ideas and cross cutting concepts. The font used in the LLPE indicates the source/alignment of each piece of the text used in the statement as it relates to the NGSS dimensions: alignment to Science and Engineering Practice(s) , alignment to Cross-Cutting Concept(s) , and alignment to the Disciplinary Core Ideas . Each unit includes a table that summarizes opportunities in each lesson for assessing every lesson-level performance expectation (LLPE). Examples of these opportunities include student handouts, home learning assignments, progress trackers, or student discussions. Most LLPEs are recommended as potential formative assessments. Assessing every LLPE listed for each student can be logistically difficult. Strategically picking which LLPEs to assess and how to provide timely and informative feedback to students on their progress toward meeting these is left to the teacher's discretion. However, the system is designed to support a quick review of the LLPE, assessment guidance, and a subset of student work to help inform instructional decisions throughout the unit even if you are not assessing each student individually every time. | |
| ... |
|